BMI Calculator - Body Mass Index Calculator
Calculate your BMI and understand your body mass index with our comprehensive calculator
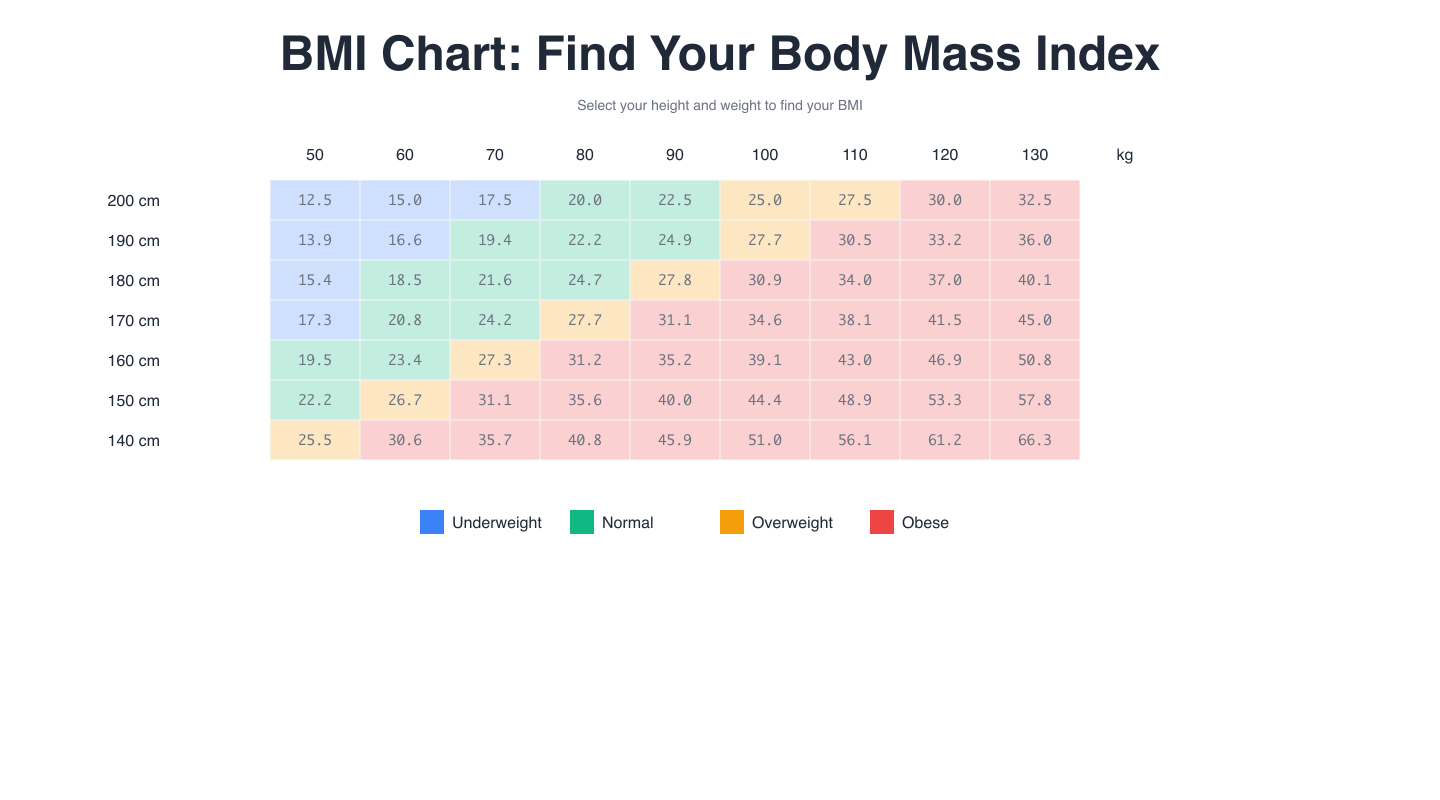
BMI Categories

BMI Chart
How is BMI Calculated?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is calculated using a simple mathematical formula that relates your weight to your height. The formula varies slightly depending on the unit system used:
BMI Formula
Metric System (kg, cm):
BMI = weight (kg) / (height (m))²
Example: Weight = 70 kg, Height = 1.75 m → BMI = 70 / (1.75)² = 22.86
Imperial System (lbs, inches):
BMI = (weight (lbs) × 703) / (height (inches))²
Example: Weight = 154 lbs, Height = 69 in → BMI = (154 × 703) / (69)² = 22.75
Understanding BMI Categories
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines standard BMI categories based on extensive research correlating BMI ranges with health risks:
- Underweight (BMI < 18.5): May indicate malnutrition or underlying health issues
- Normal Weight (BMI 18.5-24.9): Associated with lowest health risk
- Overweight (BMI 25-29.9): Increased risk for certain health conditions
- Obese (BMI ≥ 30): Significantly elevated health risks
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a healthy BMI range?
For most adults, a healthy BMI falls between 18.5 and 24.9. However, BMI is just one indicator of health. Factors like muscle mass, bone density, and overall body composition should also be considered. Athletes and bodybuilders may have higher BMIs due to increased muscle mass while still being healthy.
Is BMI accurate for everyone?
BMI has limitations and may not be accurate for everyone. It doesn't distinguish between muscle and fat mass, making it less reliable for athletes, bodybuilders, pregnant women, and elderly individuals. BMI also doesn't account for ethnic differences in body composition. For a more comprehensive health assessment, consult with a healthcare provider who can consider additional factors like waist circumference, body fat percentage, and overall health markers.
How can I improve my BMI?
Improving your BMI involves achieving a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity. Focus on consuming whole foods, maintaining a calorie deficit (if overweight) or surplus (if underweight), and incorporating both cardiovascular exercise and strength training. Sustainable lifestyle changes are more effective than crash diets. Always consult a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before starting any weight loss or weight gain program.
Should children use the same BMI calculator?
No, children and teenagers should use age and gender-specific BMI percentile charts rather than adult BMI categories. Children's body composition changes significantly as they grow, and BMI interpretation must account for developmental stages. Pediatric BMI calculators compare a child's BMI to other children of the same age and gender. Consult a pediatrician for accurate assessment of a child's healthy weight range.
What are the health risks of high or low BMI?
High BMI (overweight/obesity) is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, certain cancers, sleep apnea, and joint problems. Low BMI (underweight) may increase risk of malnutrition, weakened immune system, osteoporosis, and fertility issues. However, BMI is just one health indicator - overall fitness, nutrition, genetics, and lifestyle factors all play crucial roles in health outcomes.
Scientific References & Guidelines
Our BMI calculator follows established medical guidelines and is based on peer-reviewed scientific research:
World Health Organization (WHO)
BMI Classification Standards - The WHO established the international BMI classification system used globally for assessing weight status in adults.
WHO Obesity and Overweight Fact Sheet →Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Comprehensive BMI guidance including calculator tools, interpretation guidelines, and health considerations for different populations.
CDC BMI Information →National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
Clinical guidelines for obesity management and BMI-based health risk assessment in adults.
NHLBI BMI Calculator →Medical Literature
Key research papers on BMI methodology and health correlations:
- Keys, A., et al. (1972). "Indices of relative weight and obesity." Journal of Chronic Diseases.
- Flegal, K.M., et al. (2013). "Association of All-Cause Mortality With Overweight and Obesity Using Standard BMI Categories." JAMA.
- Romero-Corral, A., et al. (2008). "Accuracy of body mass index in diagnosing obesity in the adult general population." International Journal of Obesity.
Medical Disclaimer: This BMI calculator is for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions regarding your health or medical conditions.
Dr. Emily ChenMD, FACP
Internal Medicine & Preventive Care
This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for medical decisions.
Related Calculators
Explore more tools in the health category
Your Privacy is Protected
All calculations are performed locally in your browser. We do not store, collect, or transmit your health data.